Loculated Pleural Effusion : Loculated Pleural Effusion Chest X Ray Page 1 Line 17qq Com - In addition, a diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis of a l > r pleural effusion was performed.
Loculated Pleural Effusion : Loculated Pleural Effusion Chest X Ray Page 1 Line 17qq Com - In addition, a diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis of a l > r pleural effusion was performed.. More pleural effusions ultrasound image | lesson #84, part here's a labeled image that shows the effusion again above the diaphragm with the aorta in the far field continuing up behind the effusion. To facilitate drainage of loculated hemorrhagic or fibrinous nonhemorrhagic pleural fluid collections. Pleural fluid ldh > two thirds of upper limit for serum ldh. Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal. In transudative effusion, specific gravity is below 1.015 and.
Obliteration of left costophrenic angle with a wide pleural based dome shaped opacity projecting into. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Us scan they can be identified clearly and it is very. Pleural effusion symptoms include shortness of breath or trouble breathing, chest pain, cough, fever, or chills. Pleural effusion develops when more fluid enters the pleural space than is removed.

Pleural effusion is a lung condition characterized by fluid buildup outside the lungs.
Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal. Learn about pleural effusion including causes of pleural effusion. … differentiation of loculated effusions from solid masses. Pleural fluid is physiologically produced at. In addition, a diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis of a l > r pleural effusion was performed. Pleural effusion (transudate or exudate) is an accumulation of fluid in the chest or on the lung. Pleural fluid ldh > two thirds of upper limit for serum ldh. Pleural effusions can loculate as a result of adhesions. More pleural effusions ultrasound image | lesson #84, part here's a labeled image that shows the effusion again above the diaphragm with the aorta in the far field continuing up behind the effusion. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. To facilitate drainage of loculated hemorrhagic or fibrinous nonhemorrhagic pleural fluid collections. In transudative effusion, specific gravity is below 1.015 and. Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures.
Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. Pleural effusion with segmental and lobar opacities. .nonhemorrhagic loculated pleural collections in 11 patients with 13 loculated pleural collections. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. no change in position of effusion withchange in.
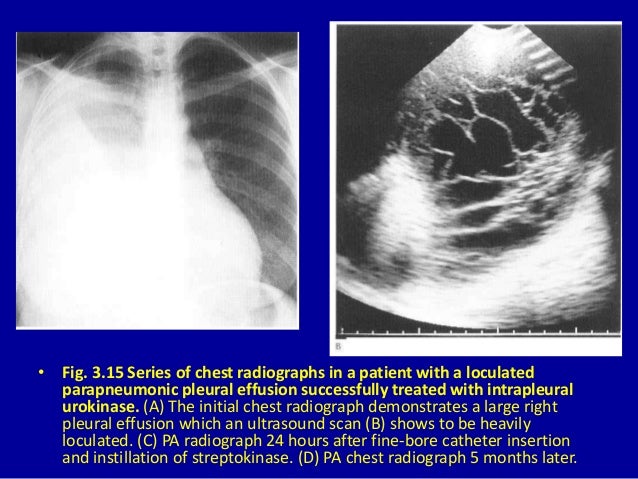
.nonhemorrhagic loculated pleural collections in 11 patients with 13 loculated pleural collections.
Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudate and exudate based on the light criteria. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Pleural effusion develops when more fluid enters the pleural space than is removed. Pleural effusions can loculate as a result of adhesions. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. no change in position of effusion withchange in. Pleural fluid is physiologically produced at. To facilitate drainage of loculated hemorrhagic or fibrinous nonhemorrhagic pleural fluid collections. In transudative effusion, specific gravity is below 1.015 and. Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. loculation occurs 2° pleural adhesions. .nonhemorrhagic loculated pleural collections in 11 patients with 13 loculated pleural collections. Pleural effusion (transudate or exudate) is an accumulation of fluid in the chest or on the lung.
no change in position of effusion withchange in. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. In addition, a diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis of a l > r pleural effusion was performed. … differentiation of loculated effusions from solid masses.
Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal.
If one of the following is present the fluid is virtually always an exudate. Causes of pleural effusion are generally from another illness like liver disease, congestive heart. Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudate and exudate based on the light criteria. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Learn about different types of pleural effusions, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. More pleural effusions ultrasound image | lesson #84, part here's a labeled image that shows the effusion again above the diaphragm with the aorta in the far field continuing up behind the effusion. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. If none is present the fluid is virtually always a transudate. Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal. The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the. .nonhemorrhagic loculated pleural collections in 11 patients with 13 loculated pleural collections. Learn about pleural effusion (fluid in the lung) symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain. My pleural effusion healed without treatment.

Komentar
Posting Komentar